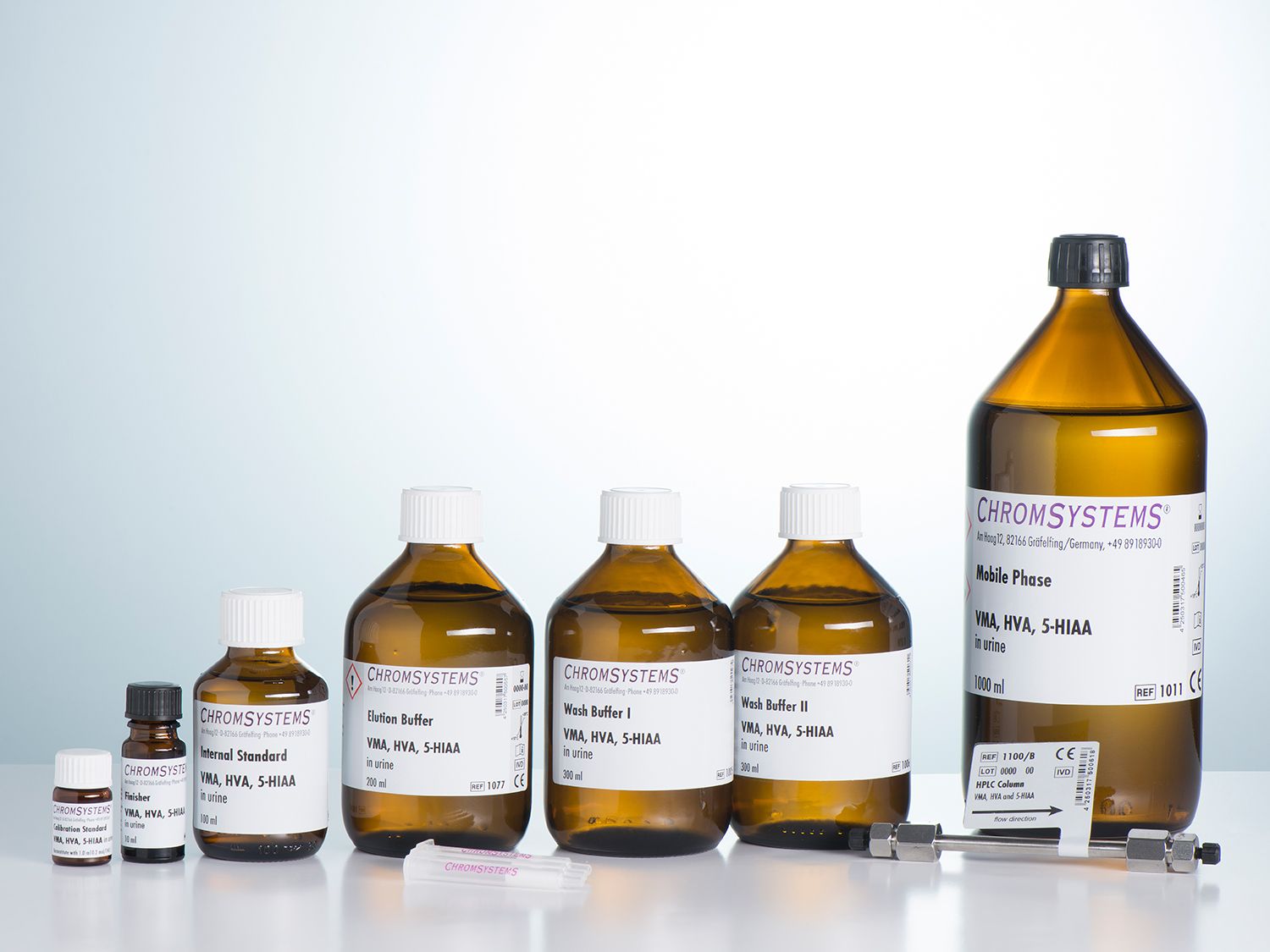
VMA, HVA, 5-HIAA in Urine - HPLC
No pH-adjustment necessary
Two internal standards available
Suitable for automated sample preparation
CE-IVD validated product ready for IVDR within timeframes and transition periods specified by the IVDR 2017/746
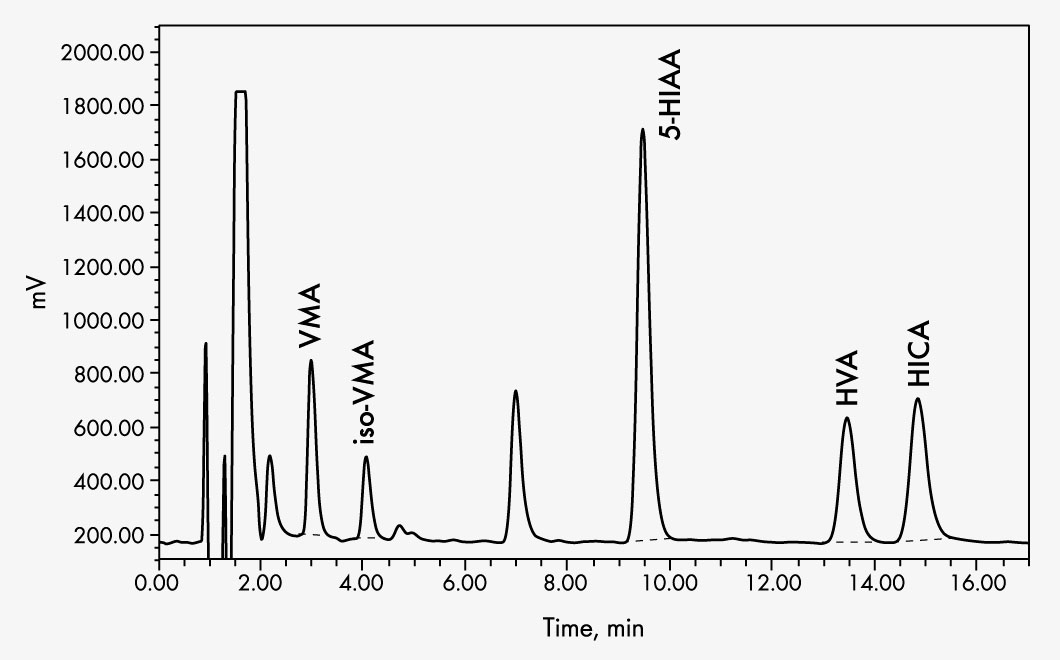

5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid (5-HIAA)
Homovanillic Acid (HVA)
Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA)
Clinical Relevance
Neuroblastoma is a neoplastic disease that is among the most common malignant cancers occurring during childhood. It is a neuroendocrine tumour resulting in higher excretion of the catecholamine metabolites vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and homovanillic acid (HVA) in the urine. Therefore verification of these parameters is critical in the diagnosis of neuroblastoma.
In contrast, increased concentrations of hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) detected in the urine are an indication of a carcinoid tumour. The malignant reproduction of enterochromaffin cells in the gastrointestinal tract leads to increased production of the tissue hormone serotonin, whose primary metabolite is 5-HIAA.
This assay allows the quantitative detection of vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), homovanillic acid (HVA) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in human urine samples via high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. The assay is used as a test for patients in whom the urine levels of these metabolites are of clinical importance.
Product advantages
• No pH-adjustment necessary
• Two internal standards available
• Automated sample preparation for Gilson® ASPEC® is available
Assay characteristics
Prior to chromatographic separation, the analytes are separated from the urine matrix by ion exchange – Sample Clean Up columns ensure easy sample preparation.
Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 100 |
| Please note | The information listed here, including the sample preparation, is not sufficient for using the product. Please read the information provided in the instruction manual, which includes detailed information on limitations associated with the use of the product in line with its intended purpose. Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual. |
| Lower and Upper Limit of Quantitation | VMA: 0.2 mg/l – 78 mg/l The LLOQ depends on the conditions of the working electrode. |
| Specimen | 24 h urine; spontaneous urine (refer the data to urine creatinine) |
| Sample Preparation | The information on the sample preparation presented here is not sufficient for use in the laboratory. For a detailed step by step description, please refer to the instruction manual.
|
| Run Time | approx. 20 min |
| Injection Volume | 10-20 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~25 °C) |
| Potential | approx. +700 mV to 850 mV |
| Additional Info | For the HPLC analysis of VMA, HVA and 5-HIAA in urine any isocratic HPLC system with electrochemical detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid (5-HIAA), Homovanillic Acid (HVA), Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) |


5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid (5-HIAA)
Homovanillic Acid (HVA)
Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA)
Clinical Relevance
Neuroblastoma is a neoplastic disease that is among the most common malignant cancers occurring during childhood. It is a neuroendocrine tumour resulting in higher excretion of the catecholamine metabolites vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and homovanillic acid (HVA) in the urine. Therefore verification of these parameters is critical in the diagnosis of neuroblastoma.
In contrast, increased concentrations of hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) detected in the urine are an indication of a carcinoid tumour. The malignant reproduction of enterochromaffin cells in the gastrointestinal tract leads to increased production of the tissue hormone serotonin, whose primary metabolite is 5-HIAA.
This assay allows the quantitative detection of vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), homovanillic acid (HVA) and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in human urine samples via high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. The assay is used as a test for patients in whom the urine levels of these metabolites are of clinical importance.
Product advantages
• No pH-adjustment necessary
• Two internal standards available
• Automated sample preparation for Gilson® ASPEC® is available
Assay characteristics
Prior to chromatographic separation, the analytes are separated from the urine matrix by ion exchange – Sample Clean Up columns ensure easy sample preparation.
Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 100 |
| Please note | The information listed here, including the sample preparation, is not sufficient for using the product. Please read the information provided in the instruction manual, which includes detailed information on limitations associated with the use of the product in line with its intended purpose. Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual. |
| Lower and Upper Limit of Quantitation | VMA: 0.2 mg/l – 78 mg/l The LLOQ depends on the conditions of the working electrode. |
| Specimen | 24 h urine; spontaneous urine (refer the data to urine creatinine) |
| Sample Preparation | The information on the sample preparation presented here is not sufficient for use in the laboratory. For a detailed step by step description, please refer to the instruction manual.
|
| Run Time | approx. 20 min |
| Injection Volume | 10-20 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~25 °C) |
| Potential | approx. +700 mV to 850 mV |
| Additional Info | For the HPLC analysis of VMA, HVA and 5-HIAA in urine any isocratic HPLC system with electrochemical detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid (5-HIAA), Homovanillic Acid (HVA), Vanillylmandelic Acid (VMA) |