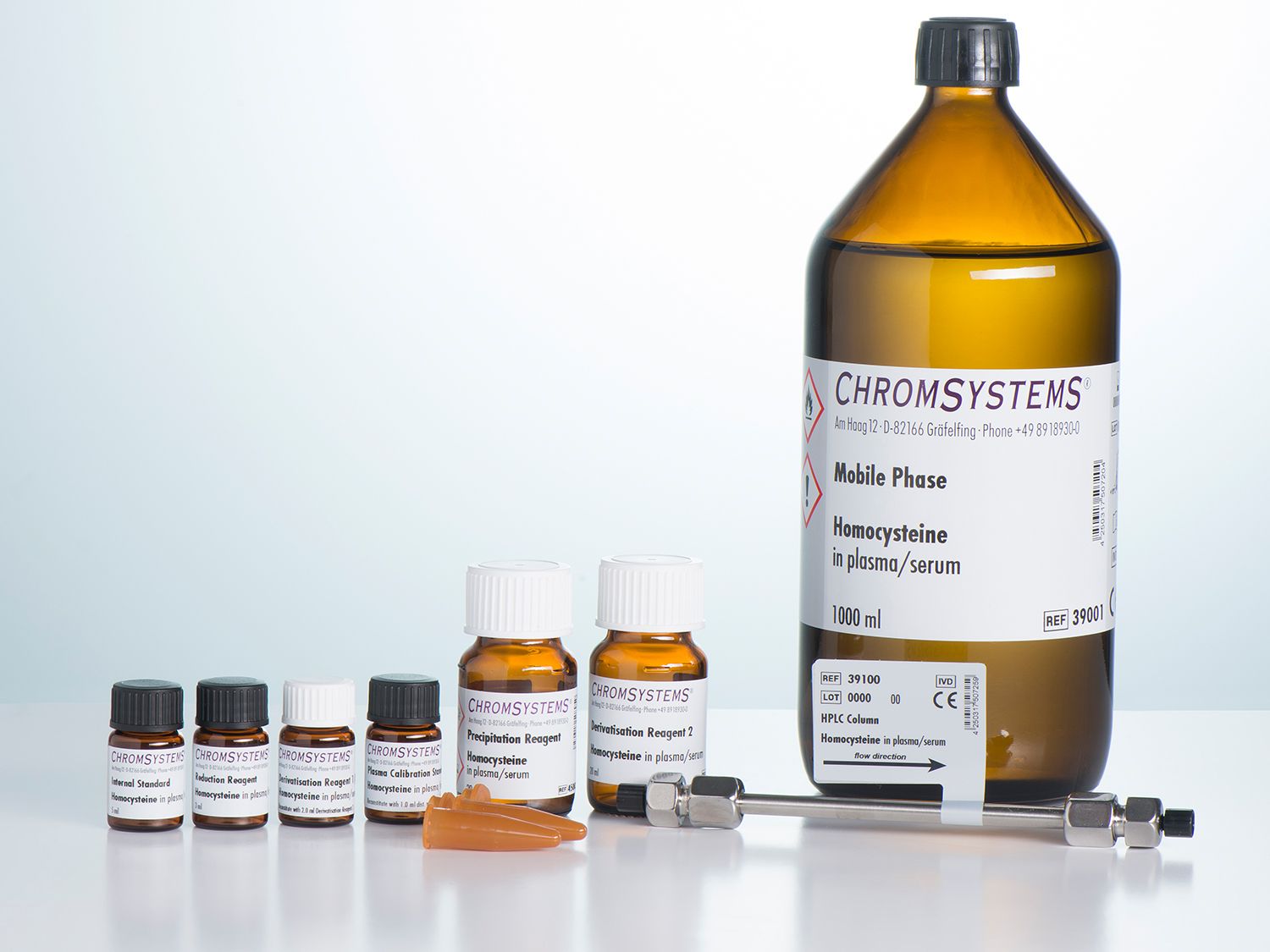
Homocysteine in Plasma/Serum - HPLC
Fast sample preparation
Short analysis time
Column life-time more than 2000 runs
Suitable for all blood collection systems
CE-IVD validated product ready for IVDR within timeframes and transition periods specified by the IVDR 2017/746

Homocysteine
Clinical relevance
Homocysteine (Hcy) is a non-proteinogenic amino acid, synthesized during the demethylation of the amino acid methionine. Some enzymes are involved in this process, which require cofactors such as vitamin B6 and vitamin B12. A deficiency of these cofactors can lead to an increase in the Hcy concentration, but inherited genetic mutations may also be the cause.
Even moderately increased Hcy levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, arteriosclerosis and coronary heart diseases. Increased Hcy levels are also detected in the case of homocystinuria, an inherited genetic disorder in which the enzymes required for metabolism are not present or at levels that are too low. In this case, already newborns have high levels of Hcy, however, the disease is treatable if detected in time. Screening of newborns (NBS) for homocystinuria has therefore become mandatory in some European countries such as Ireland. In Germany it is only performed as part of more intensive screening or in cases where the disease is suspected.
Product advantages
- Fast sample preparation
- Short analysis time
- Column lifetime of more than 2000 runs
- For all blood collection systems
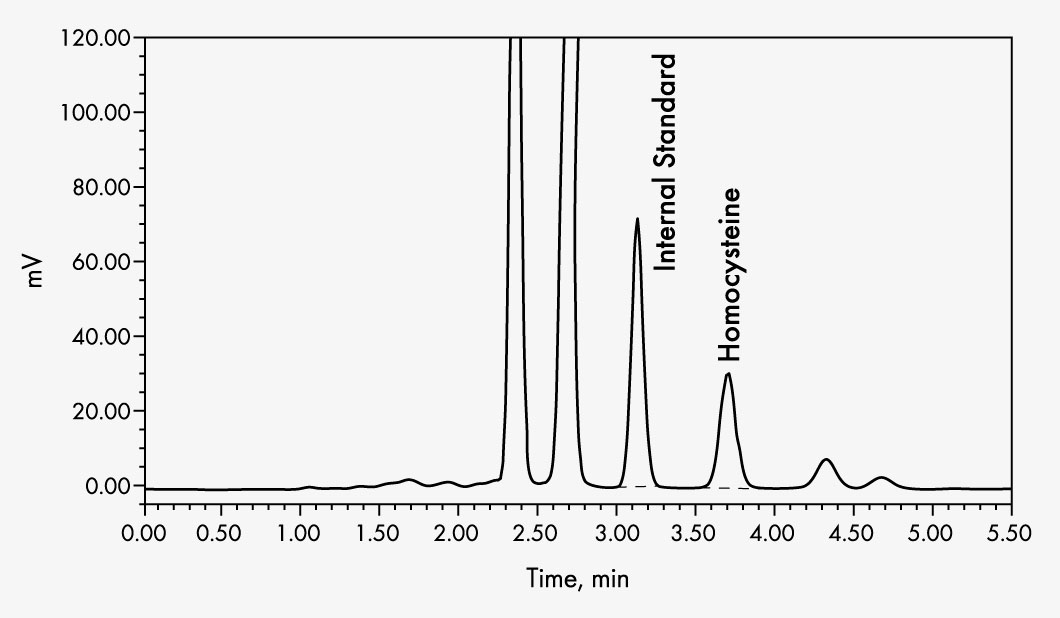
This assay allows the simple and reliable determination of total homocysteine in serum/plasma. Sample preparation is simply a reduction step for releasing homocysteine from its protein binding, followed by precipitation and subsequent precolumn derivatisation. Chromatographic separation is performed on an isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detection. The optimised reagents ensure the accurate and reliable quantification of total homocysteine for all blood collection systems within a brief analysis period of less than 6 minutes.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 200 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | 0.4 µmol/l |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | up to 400 µmol/l |
| Intraassay | CV = 0.9–2.2 % |
| Interassay | CV = 2.9–3.1 % |
| Recovery | 96–99 % |
| Specimen | Plasma/Serum |
| Sample Preparation |
|
| Run Time | 5.5 min |
| Injection Volume | 20–50 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1.3–1.7 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~ 25 °C) |
| Wavelengths | EX 385 nm |
| Additional Info | Any isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Homocysteine |


Homocysteine
Clinical relevance
Homocysteine (Hcy) is a non-proteinogenic amino acid, synthesized during the demethylation of the amino acid methionine. Some enzymes are involved in this process, which require cofactors such as vitamin B6 and vitamin B12. A deficiency of these cofactors can lead to an increase in the Hcy concentration, but inherited genetic mutations may also be the cause.
Even moderately increased Hcy levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, arteriosclerosis and coronary heart diseases. Increased Hcy levels are also detected in the case of homocystinuria, an inherited genetic disorder in which the enzymes required for metabolism are not present or at levels that are too low. In this case, already newborns have high levels of Hcy, however, the disease is treatable if detected in time. Screening of newborns (NBS) for homocystinuria has therefore become mandatory in some European countries such as Ireland. In Germany it is only performed as part of more intensive screening or in cases where the disease is suspected.
Product advantages
- Fast sample preparation
- Short analysis time
- Column lifetime of more than 2000 runs
- For all blood collection systems
This assay allows the simple and reliable determination of total homocysteine in serum/plasma. Sample preparation is simply a reduction step for releasing homocysteine from its protein binding, followed by precipitation and subsequent precolumn derivatisation. Chromatographic separation is performed on an isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detection. The optimised reagents ensure the accurate and reliable quantification of total homocysteine for all blood collection systems within a brief analysis period of less than 6 minutes.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 200 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | 0.4 µmol/l |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | up to 400 µmol/l |
| Intraassay | CV = 0.9–2.2 % |
| Interassay | CV = 2.9–3.1 % |
| Recovery | 96–99 % |
| Specimen | Plasma/Serum |
| Sample Preparation |
|
| Run Time | 5.5 min |
| Injection Volume | 20–50 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1.3–1.7 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~ 25 °C) |
| Wavelengths | EX 385 nm |
| Additional Info | Any isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Homocysteine |