Hemoglobin Variants - HPLC
All important hemoglobin variants within 9 min.
Improved sample throughput and efficiency
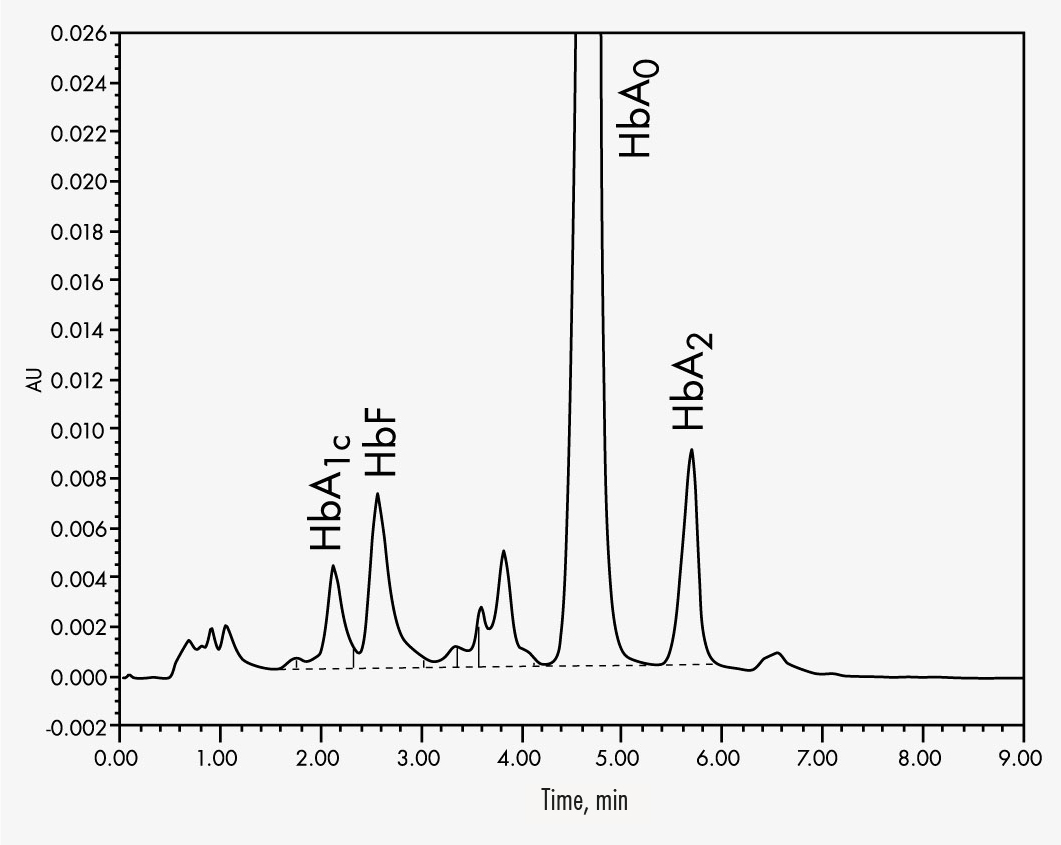

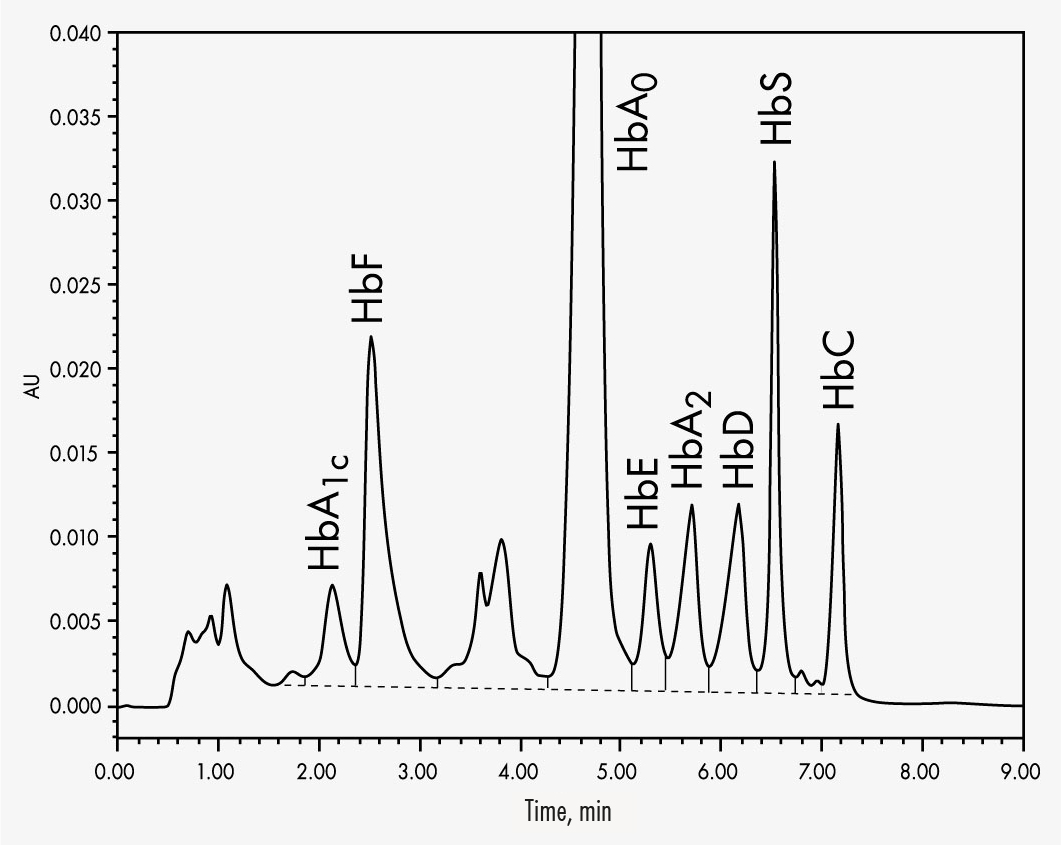

HbA
HbA1c
HbA2
HbC
HbD
HbE
HbF
HbS
Clinical relevance
The haemoglobin molecule is responsible for transporting oxygen inside of the human organism, and consists of four globin polypeptide chains and one haem molecule. In humans, the globin polypeptide chains are further subdivided in α, β, γ and δ chains. Human haemoglobin usually consists of two α chains and two additional globin chains (β, γ or δ). In adults, the major component of haemoglobin is HbA (ααββ). Its glycated forms are referred to as HbA1a, HbA1b and HbA1c. HbA2 consists of two α chains and two δ chains. Foetal haemoglobin (HbF) consists of two α chains and two β chains.
Genetic disorders of haemoglobin production are called thalassaemias – they most commonly affect the β chain. This leads to β-thalassaemia. It is especially common in populations in the Mediterranean region, the Middle East and East Asia, but it also occurs in Middle Europe and North America as a result of demographic change.
Product advantages
- Measurement of all key haemoglobin variants in just 9 minutes
- Clear identifiable peaks and reliable values
By making use of the high separating capacities of the analytical column, the Chromsystems assay for the analysis of haemoglobin variants can determine the most common variants HbA1c, HbA2, HbC, HbD, HbE, HbF and HbS within 9 minutes. A column material specially designed for this specific separation process also allows a stable separation of HbA2 from HbD and HbE even with aged columns. This helps to eliminate false quantifications and qualifications.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 1000 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | HbA2: 2 % |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | HbA2: up to at least 75 % |
| Intraassay | CV < 8 % |
| Interassay | CV < 4 % |
| Recovery | HbA2: 100 %; HbF: 99 % |
| Specimen | Whole blood |
| Sample Preparation |
|
| Run Time | 9 min |
| Injection Volume | 10-20 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1.5 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient temperature (~ 25 °C) |
| Gradient | binary |
| Wavelengths | 415 nm |
| Additional Info | Any HPLC gradient system with UV/VIS detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | HbA, HbA1c, HbA2, HbC, HbD, HbE, HbF, HbS |
| Pressure | Maximum pressure: 140 bar |




HbA
HbA1c
HbA2
HbC
HbD
HbE
HbF
HbS
Clinical relevance
The haemoglobin molecule is responsible for transporting oxygen inside of the human organism, and consists of four globin polypeptide chains and one haem molecule. In humans, the globin polypeptide chains are further subdivided in α, β, γ and δ chains. Human haemoglobin usually consists of two α chains and two additional globin chains (β, γ or δ). In adults, the major component of haemoglobin is HbA (ααββ). Its glycated forms are referred to as HbA1a, HbA1b and HbA1c. HbA2 consists of two α chains and two δ chains. Foetal haemoglobin (HbF) consists of two α chains and two β chains.
Genetic disorders of haemoglobin production are called thalassaemias – they most commonly affect the β chain. This leads to β-thalassaemia. It is especially common in populations in the Mediterranean region, the Middle East and East Asia, but it also occurs in Middle Europe and North America as a result of demographic change.
Product advantages
- Measurement of all key haemoglobin variants in just 9 minutes
- Clear identifiable peaks and reliable values
By making use of the high separating capacities of the analytical column, the Chromsystems assay for the analysis of haemoglobin variants can determine the most common variants HbA1c, HbA2, HbC, HbD, HbE, HbF and HbS within 9 minutes. A column material specially designed for this specific separation process also allows a stable separation of HbA2 from HbD and HbE even with aged columns. This helps to eliminate false quantifications and qualifications.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 1000 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | HbA2: 2 % |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | HbA2: up to at least 75 % |
| Intraassay | CV < 8 % |
| Interassay | CV < 4 % |
| Recovery | HbA2: 100 %; HbF: 99 % |
| Specimen | Whole blood |
| Sample Preparation |
|
| Run Time | 9 min |
| Injection Volume | 10-20 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1.5 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient temperature (~ 25 °C) |
| Gradient | binary |
| Wavelengths | 415 nm |
| Additional Info | Any HPLC gradient system with UV/VIS detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | HbA, HbA1c, HbA2, HbC, HbD, HbE, HbF, HbS |
| Pressure | Maximum pressure: 140 bar |




