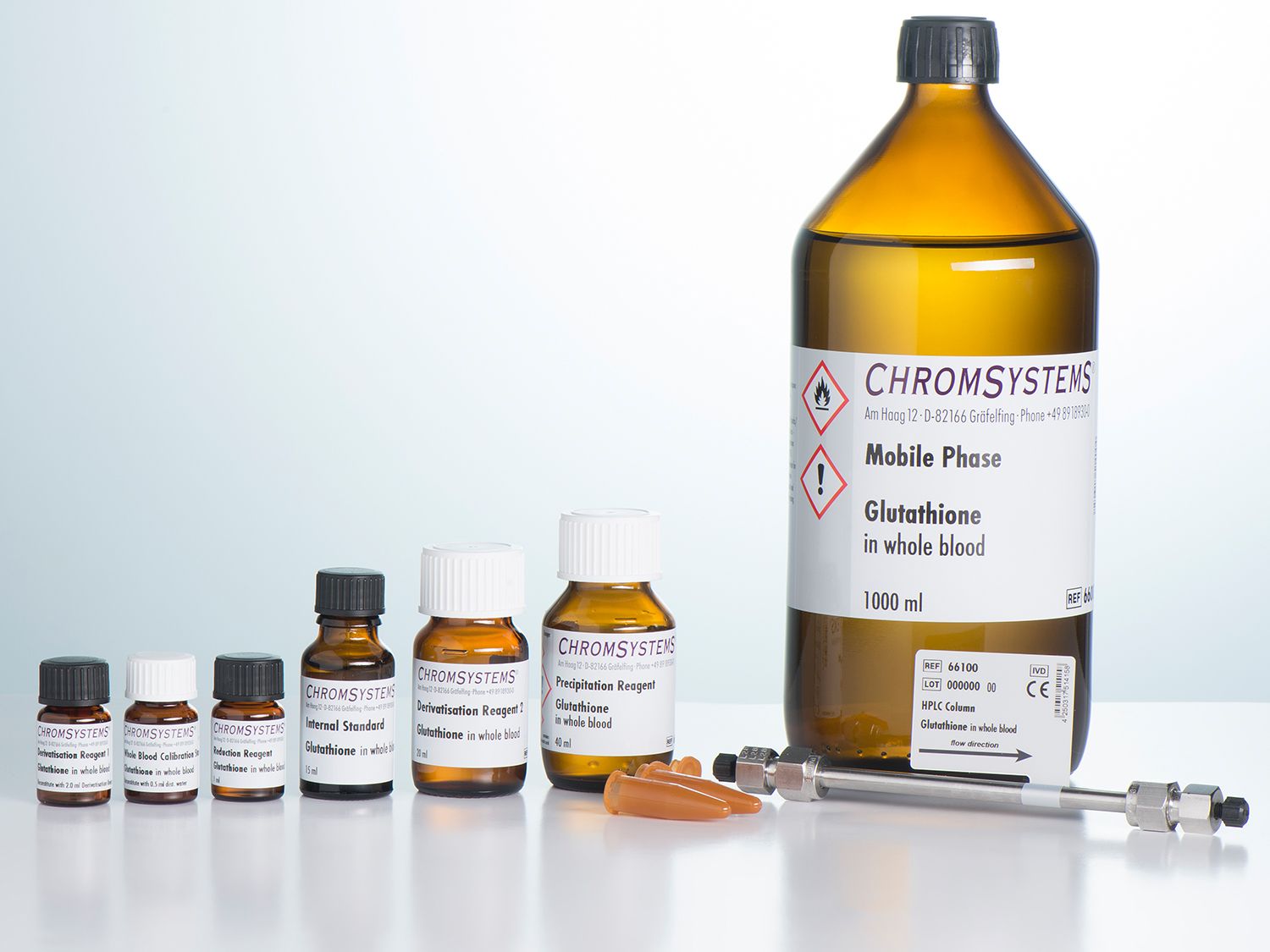
Glutathione in Whole Blood - HPLC
Detection of reduced and oxidized form
10 µl sample volume
High reliability by inclusion of an internal standard
CE-IVD validated product ready for IVDR within timeframes and transition periods specified by the IVDR 2017/746

Free Glutathione (GSH)
Glutathionedisulfide (GSSG)
Clinical relevance
Glutathione is a tripeptide, which is present in nearly all cells at high concentrations and is one of the most important antioxidant substances in the body. Glutathione exists in a reduced (GSH) and an oxidized form (GSSG) and the ratio of both is a measure for the redox status of the cell. Glutathione is especially important for the erythrocytes. Here it is involved in reducing methaemoglobin to haemoglobin, which can then bind oxygen molecules once again. Glutathione is also required for many reductive reactions in the body cells, thereby regulating the concentration of free radicals. Glutathione forms conjugates in the liver that eliminate toxic contaminants. There it also inactivates reactive intermediate products resulting from the metabolisation of certain drugs. Therefore, a high concentration of GSSG can indicate a liver necrosis or dystrophy.
Product advantages
- Detection of reduced and oxidised form
- Sample volume of only 10 µl is sufficient
- High reliability by using an internal standard
GSH as well as GSSG can be reliably quantified with this Chromsystems assay by using only 10 µl of whole blood. The sample preparation is based on protein precipitation and derivatisation followed by HPLC determination with fluorescence detection. After precipitation, the sample is split into two halves. One aliquot is derivatised immediately for the determination of reduced glutathione; the second aliquot is chemically reduced before derivatisation which leads to the detection of the sum of both, oxidised and reduced glutathione. The use of an optimised internal standard minimises any analytical variations that could be crucial when calculating the GSSG/GSH ratio.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 100 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | 5 µmol/l |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | up to 15000 µmol/l |
| Intraassay | CV ≤ 4.6 % |
| Interassay | CV ≤ 4 % |
| Recovery | 99 % |
| Specimen | Whole Blood |
| Sample Preparation | 1) Preparation of whole blood samples:
2) Determination of free glutathione:
3) Determination of the sum of oxidised and free glutathione:
|
| Run Time | 5 min |
| Injection Volume | 20 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1.3 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~ 25 °C) |
| Gradient | Isocratic |
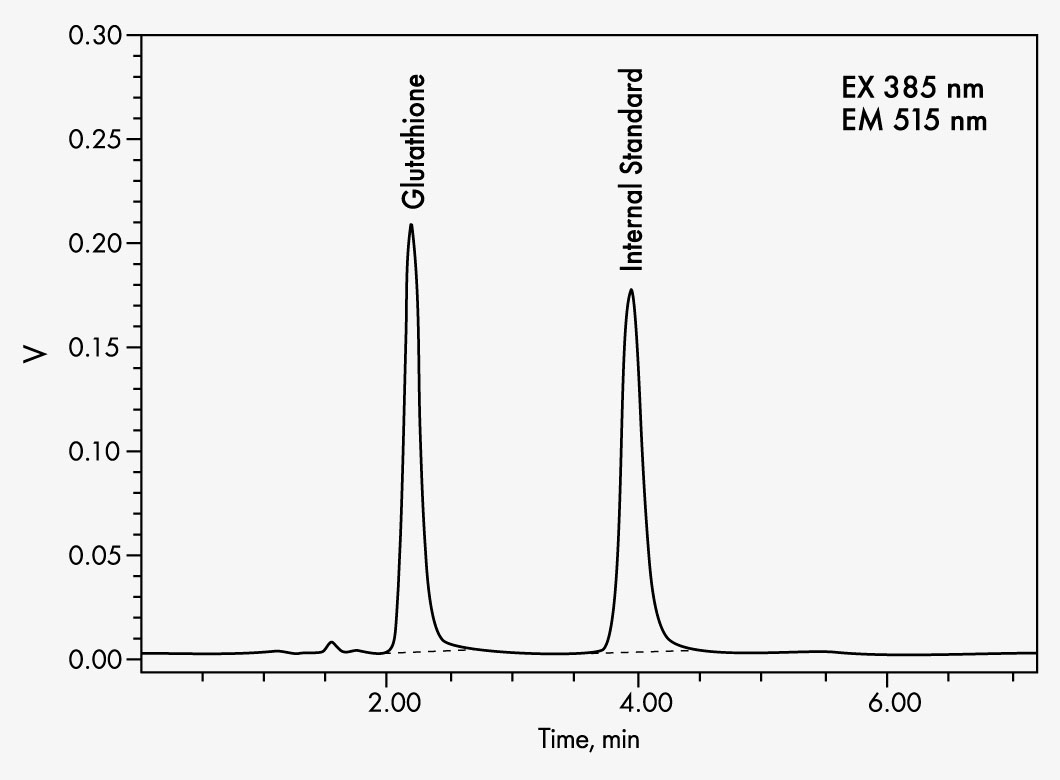
| Wavelengths | EX 385 nm, EM 515 nm |
| Additional Info | Any isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Free Glutathione (GSH), Glutathionedisulfide (GSSG) |


Free Glutathione (GSH)
Glutathionedisulfide (GSSG)
Clinical relevance
Glutathione is a tripeptide, which is present in nearly all cells at high concentrations and is one of the most important antioxidant substances in the body. Glutathione exists in a reduced (GSH) and an oxidized form (GSSG) and the ratio of both is a measure for the redox status of the cell. Glutathione is especially important for the erythrocytes. Here it is involved in reducing methaemoglobin to haemoglobin, which can then bind oxygen molecules once again. Glutathione is also required for many reductive reactions in the body cells, thereby regulating the concentration of free radicals. Glutathione forms conjugates in the liver that eliminate toxic contaminants. There it also inactivates reactive intermediate products resulting from the metabolisation of certain drugs. Therefore, a high concentration of GSSG can indicate a liver necrosis or dystrophy.
Product advantages
- Detection of reduced and oxidised form
- Sample volume of only 10 µl is sufficient
- High reliability by using an internal standard
GSH as well as GSSG can be reliably quantified with this Chromsystems assay by using only 10 µl of whole blood. The sample preparation is based on protein precipitation and derivatisation followed by HPLC determination with fluorescence detection. After precipitation, the sample is split into two halves. One aliquot is derivatised immediately for the determination of reduced glutathione; the second aliquot is chemically reduced before derivatisation which leads to the detection of the sum of both, oxidised and reduced glutathione. The use of an optimised internal standard minimises any analytical variations that could be crucial when calculating the GSSG/GSH ratio.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 100 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | 5 µmol/l |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | up to 15000 µmol/l |
| Intraassay | CV ≤ 4.6 % |
| Interassay | CV ≤ 4 % |
| Recovery | 99 % |
| Specimen | Whole Blood |
| Sample Preparation | 1) Preparation of whole blood samples:
2) Determination of free glutathione:
3) Determination of the sum of oxidised and free glutathione:
|
| Run Time | 5 min |
| Injection Volume | 20 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1.3 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~ 25 °C) |
| Gradient | Isocratic |
| Wavelengths | EX 385 nm, EM 515 nm |
| Additional Info | Any isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Free Glutathione (GSH), Glutathionedisulfide (GSSG) |