Catecholamines in Plasma - HPLC
Easy sample preparation
Low analysis costs
CE-IVD validated product ready for IVDR within timeframes and transition periods specified by the IVDR 2017/746
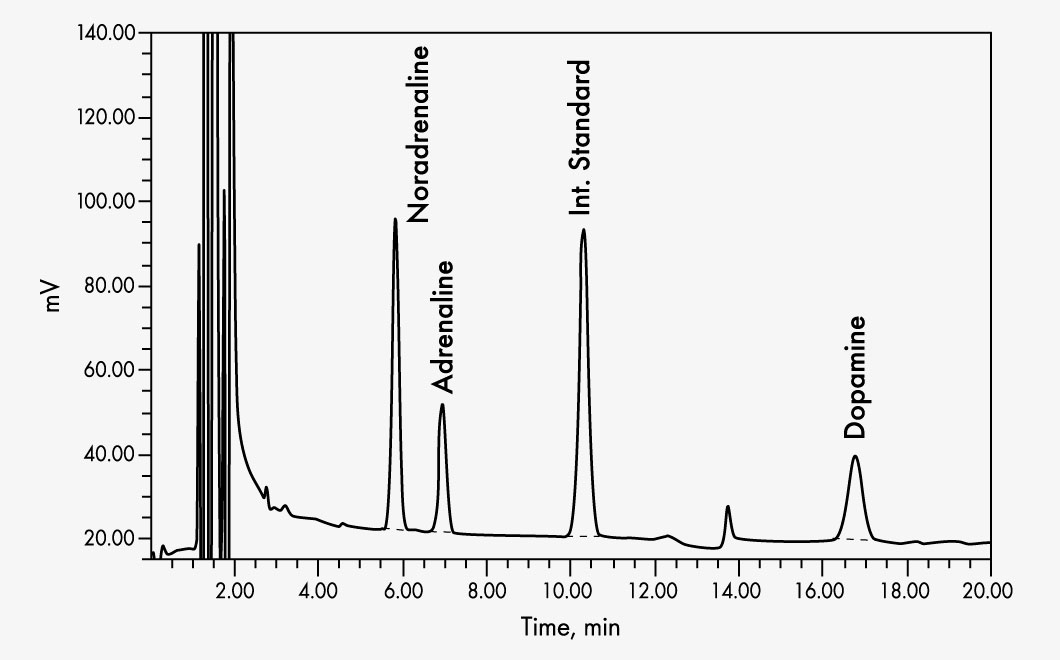

Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
Dopamine
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
Clinical relevance
The catecholamines adrenaline (epinephrine), noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and dopamine are biogenic amines, which play a central role in the body as hormones and neurotransmitters. Adrenaline and noradrenaline are produced in the adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter in the brain and acts as a local messenger substance in the peripheral nervous system.
The determination of catecholamines has clinical significance in the diagnosis of pheochromocytomas and other tumours affecting the nervous system. These diseases result in the production of surplus catecholamines, which are then excreted in the urine. 24-hour urine collection as the preferred method for tumour screening. The concentrations of adrenaline and noradrenaline are important indicators for cardiac insufficiency, cardiac diseases and arteriosclerosis.
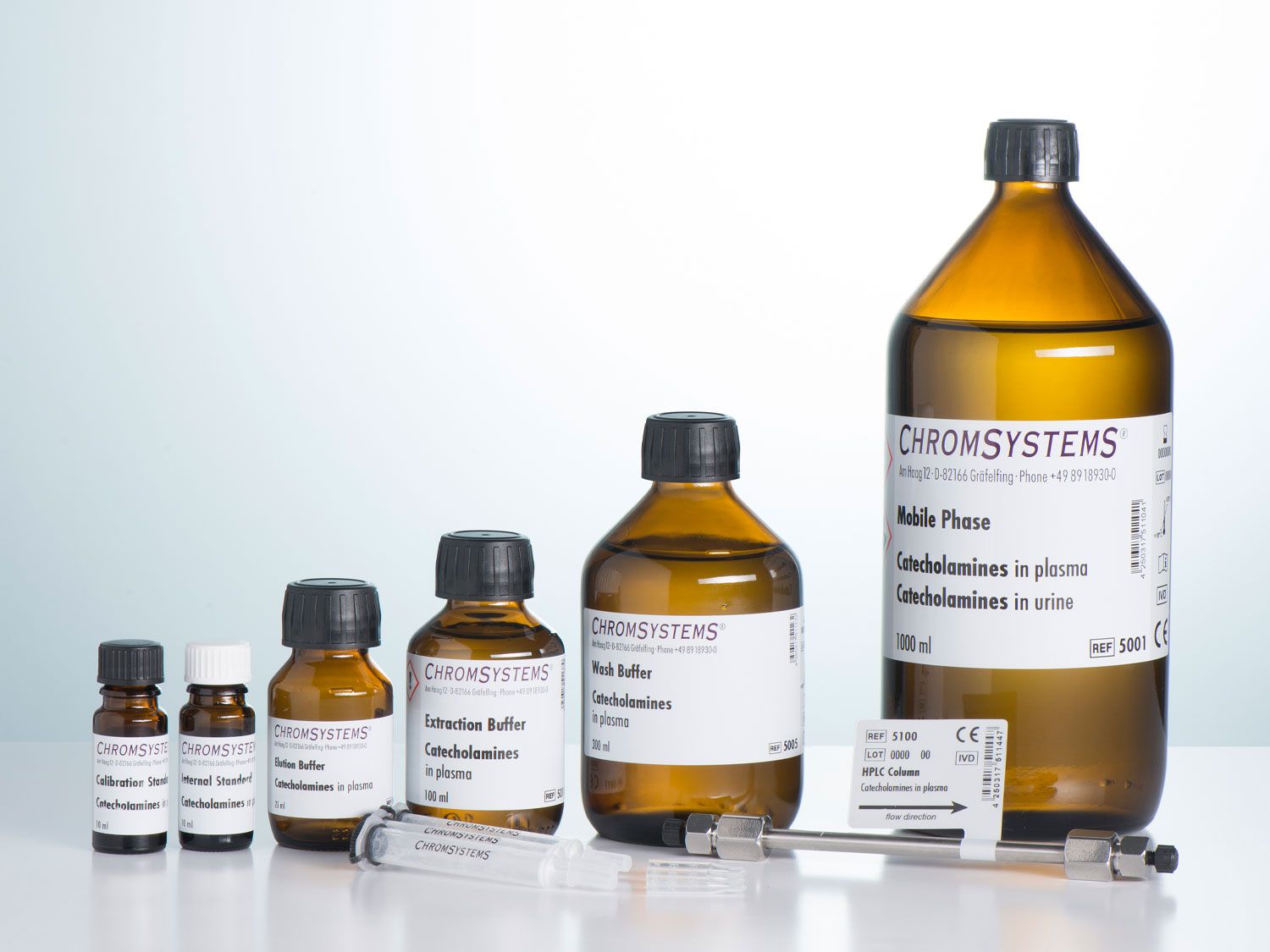
This assay allows the quantitative determination of adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine in human plasma samples via high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection.
It is intended as a monitoring test for patients with suspected catecholamine-secreting tumour.
Product advantages
• Easy sample preparation
• Low analysis costs
Assay characteristics
Before HPLC analysis, the analytes are extracted from the plasma matrix by adsorption on alumina. Sample preparation is simple, because pH-adjustment of the plasma samples is not necessary. Moreover, sample preparation requires only washing steps with Wash Buffer.
For the HPLC analysis of catecholamines in urine, there is an additional method available (order no. 6000).
Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 200 |
| Please note | The information listed here, including the sample preparation, is not sufficient for using the product. Please read the information provided in the instruction manual, which includes detailed information on limitations associated with the use of the product in line with its intended purpose. Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual. |
| Lower and Upper Limit of Quantitation | Adrenaline/Epinephrine: 18 ng/l – 2250 ng/l The limit of quantification depends on the condition of the working electrode. |
| Specimen | Plasma |
| Sample Preparation | The information on the sample preparation presented here is not sufficient for use in the laboratory. For a detailed step by step description, please refer to the instruction manual.
|
| Run Time | < 20 min |
| Injection Volume | 20-50 µl |
| Flow Rate | 0.8-1.3 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~25 °C) |
| Potential | 400 - 500 mV |
| Additional Info | For the HPLC analysis of catecholamines in plasma any isocratic HPLC system with electrochemical detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Adrenaline (Epinephrine), Dopamine, Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) |


Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
Dopamine
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
Clinical relevance
The catecholamines adrenaline (epinephrine), noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and dopamine are biogenic amines, which play a central role in the body as hormones and neurotransmitters. Adrenaline and noradrenaline are produced in the adrenal medulla and the sympathetic nervous system. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter in the brain and acts as a local messenger substance in the peripheral nervous system.
The determination of catecholamines has clinical significance in the diagnosis of pheochromocytomas and other tumours affecting the nervous system. These diseases result in the production of surplus catecholamines, which are then excreted in the urine. 24-hour urine collection as the preferred method for tumour screening. The concentrations of adrenaline and noradrenaline are important indicators for cardiac insufficiency, cardiac diseases and arteriosclerosis.
This assay allows the quantitative determination of adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine in human plasma samples via high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection.
It is intended as a monitoring test for patients with suspected catecholamine-secreting tumour.
Product advantages
• Easy sample preparation
• Low analysis costs
Assay characteristics
Before HPLC analysis, the analytes are extracted from the plasma matrix by adsorption on alumina. Sample preparation is simple, because pH-adjustment of the plasma samples is not necessary. Moreover, sample preparation requires only washing steps with Wash Buffer.
For the HPLC analysis of catecholamines in urine, there is an additional method available (order no. 6000).
Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 200 |
| Please note | The information listed here, including the sample preparation, is not sufficient for using the product. Please read the information provided in the instruction manual, which includes detailed information on limitations associated with the use of the product in line with its intended purpose. Detailed performance evaluation data for this assay can be found in the appendices of the instruction manual. |
| Lower and Upper Limit of Quantitation | Adrenaline/Epinephrine: 18 ng/l – 2250 ng/l The limit of quantification depends on the condition of the working electrode. |
| Specimen | Plasma |
| Sample Preparation | The information on the sample preparation presented here is not sufficient for use in the laboratory. For a detailed step by step description, please refer to the instruction manual.
|
| Run Time | < 20 min |
| Injection Volume | 20-50 µl |
| Flow Rate | 0.8-1.3 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~25 °C) |
| Potential | 400 - 500 mV |
| Additional Info | For the HPLC analysis of catecholamines in plasma any isocratic HPLC system with electrochemical detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Adrenaline (Epinephrine), Dopamine, Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) |